코드잇 Codeit/Python / ML / DL
[코드잇] 파이썬 프로그래밍 기초 - 파이썬 응용하기
꼽파
2023. 8. 4. 18:47

1. 파이썬 모듈 맛보기
모듈
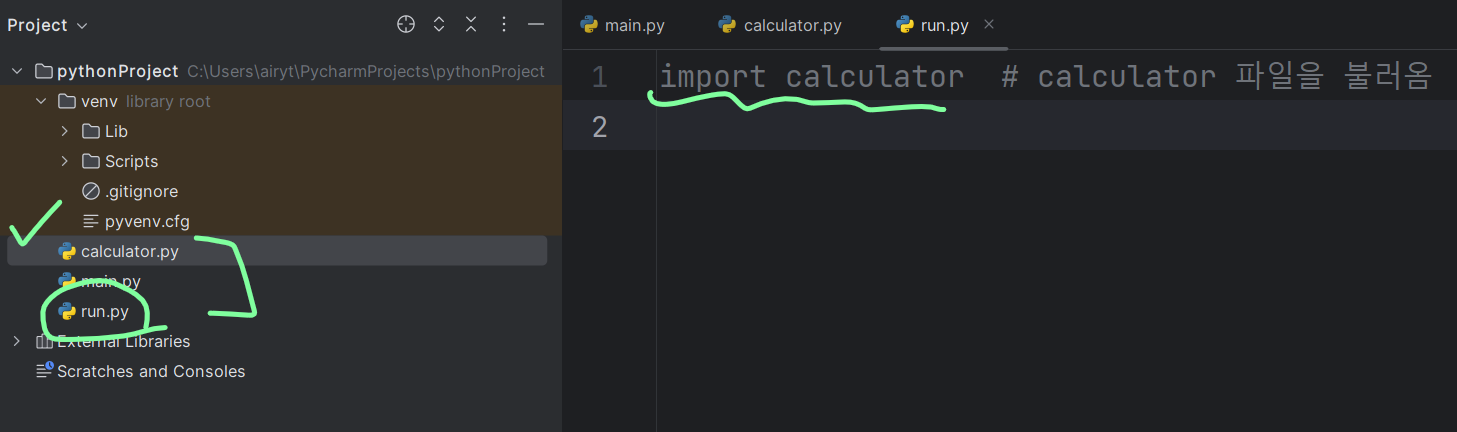
같은 폴더에 있는 파이썬 파일만 불러올 수 있음.
run.py와 calculator.py랑 같은 폴더에 있기 때문에 불러올 수 있음.
다른 폴더에 있는 파일을 불러오는 것은 다음 토픽에 나옴.
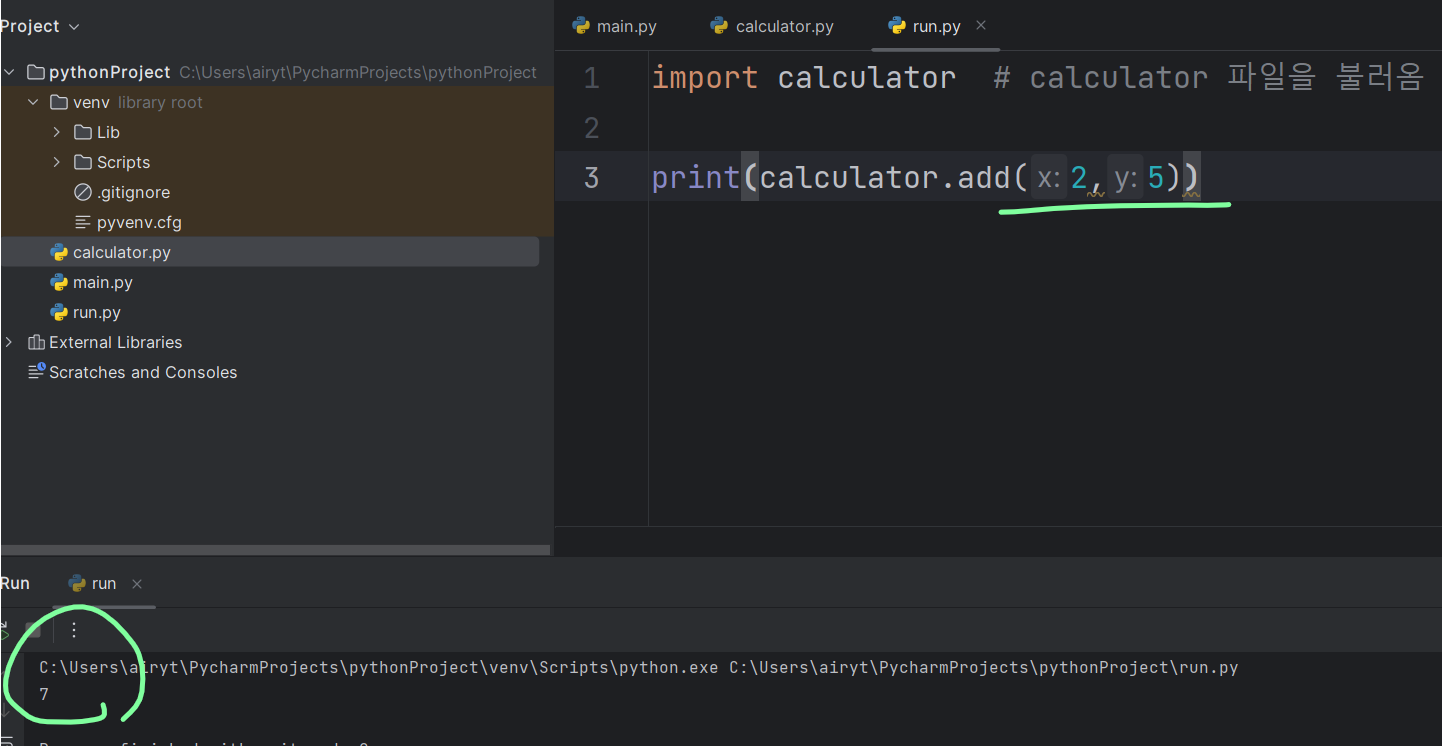
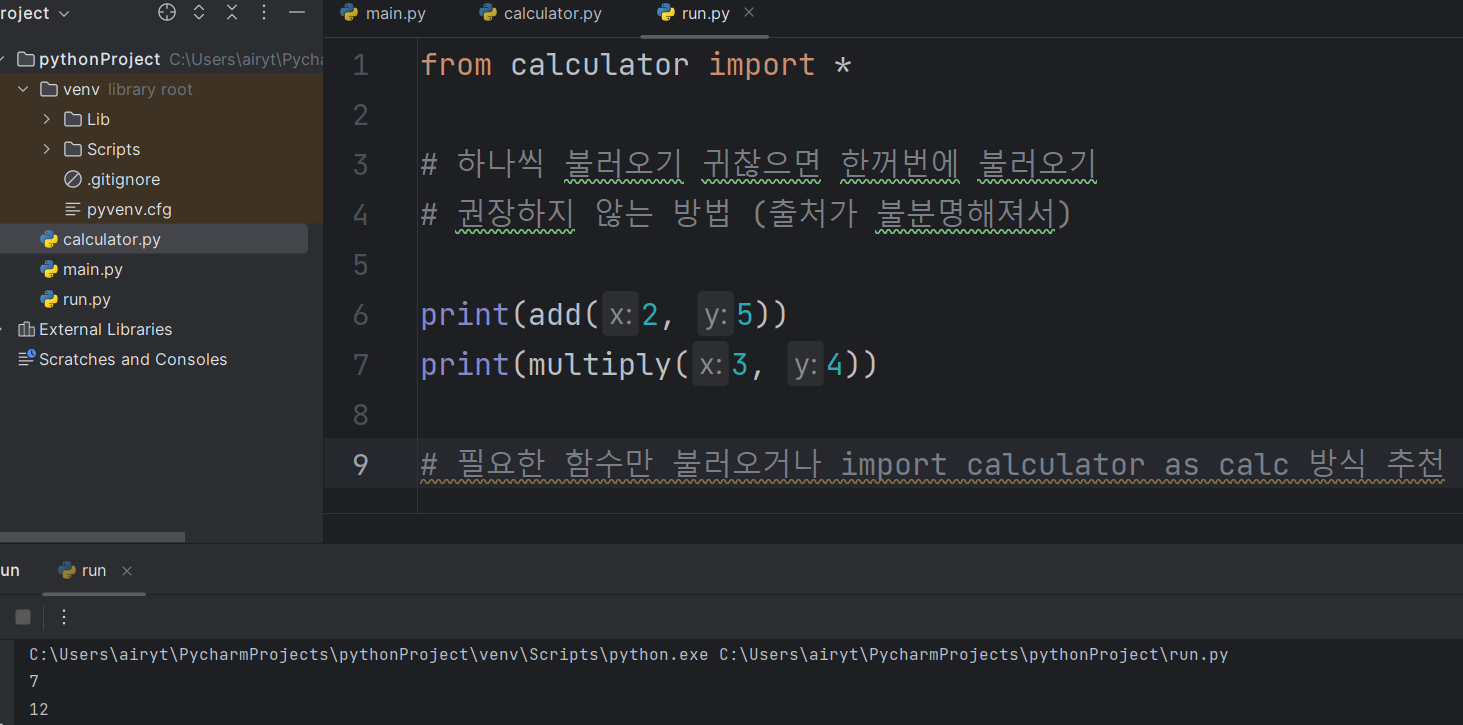
import calculator
# 같은 폴더 내에 있는 calculator 파일을 불러오기
# calculator.py 파일 = 모듈
# 다른 파이썬 프로그램에서 사용할 수 있는 파이썬 코드 = 모듈
print(calculator.add(2, 5)) # 7
print(calculator.multiply(3, 4)) # 12
###
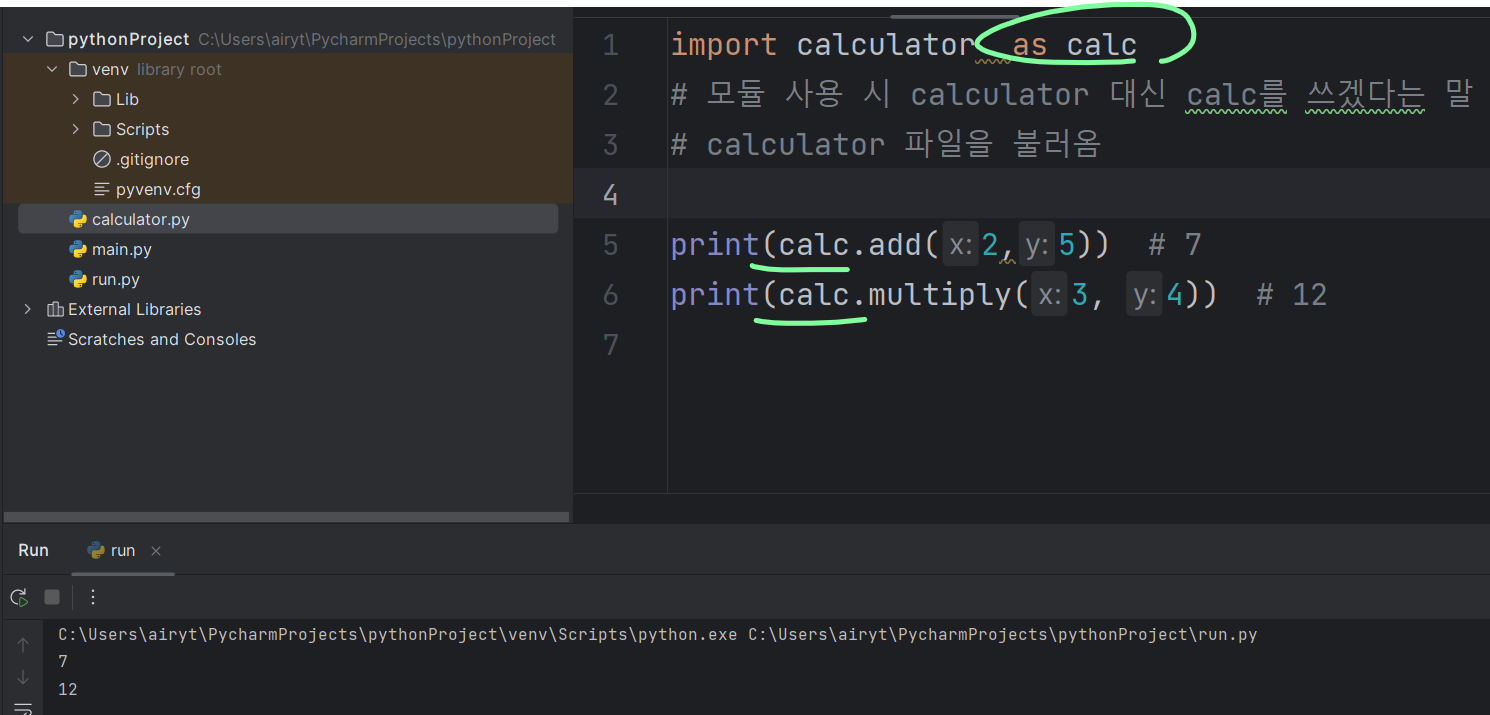
불러오는 모듈 이름을 지정
###
import calculator as calc
# as calc = 모듈 사용 시 calculator 대신 calc를 쓰겠다는 말
# calculator 파일을 불러옴
print(calc.add(2, 5)) # 7
print(calc.multiply(3, 4)) # 12
###
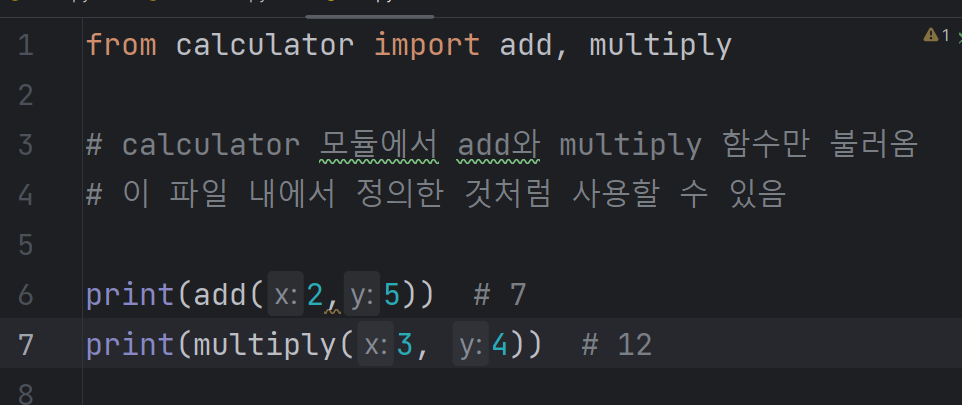
특정 모듈에서 필요한 함수만 불러오기
###
from calculator import add, multiply
# calculator에서 특정 함수(add, multiply)만 불러오기
print(add(2, 5)) # 7
print(multiply(3, 4)) # 12
# 앞에 모듈 이름 안 붙여도 됨.
# add, multiply 함수는 마치 파일 내에서 정의한 함수인 것처럼 사용할 수 있음.
###
특정 모듈에서 모든 함수 불러와서 사용하기
###
from calculator import *
# 모든 함수를 불러오라는 뜻
print(add(2, 5)) # 7
print(multiply(3, 4)) # 12
# 함수들의 출처가 불분명해서 권장하지 않음.
# 필요한 함수만 불러오거나 import calculator as calc 방식 추천
스탠다드 라이브러리
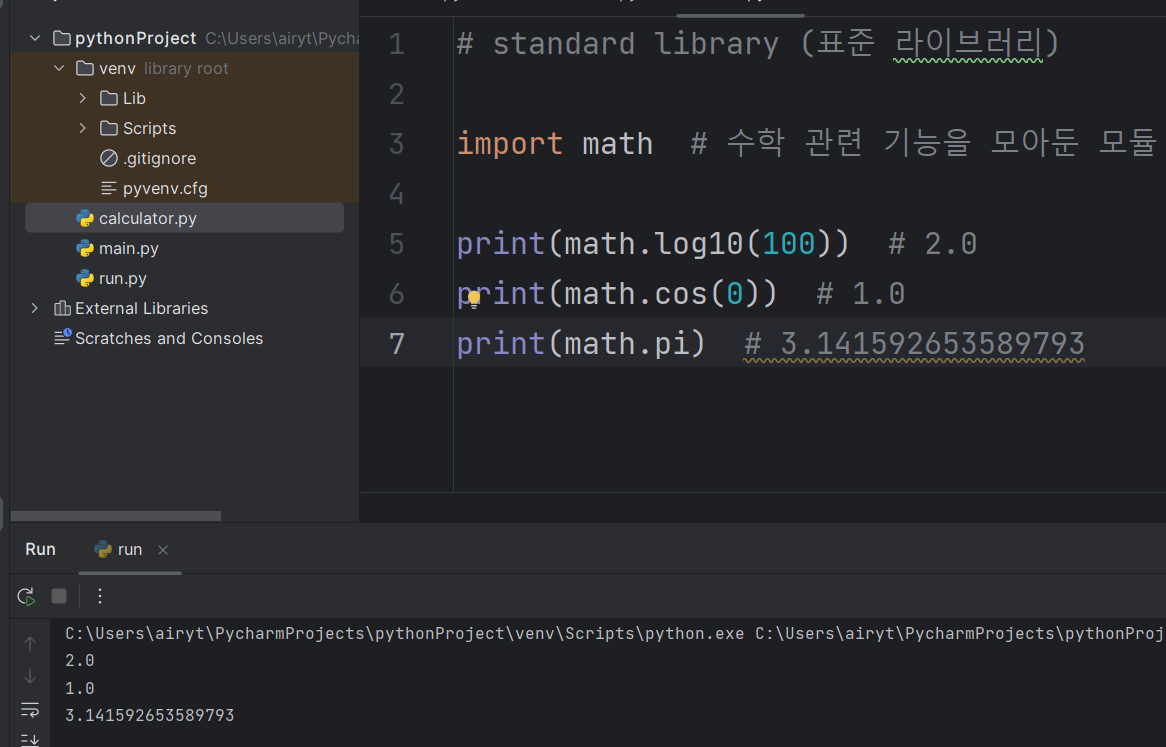
# standard library (표준 라이브러리)
import math # 수학 관련 기능을 모아둔 모듈
print(math.log10(100)) # 2.0
print(math.cos(0)) # 1.0
print(math.pi) # 3.141592653589793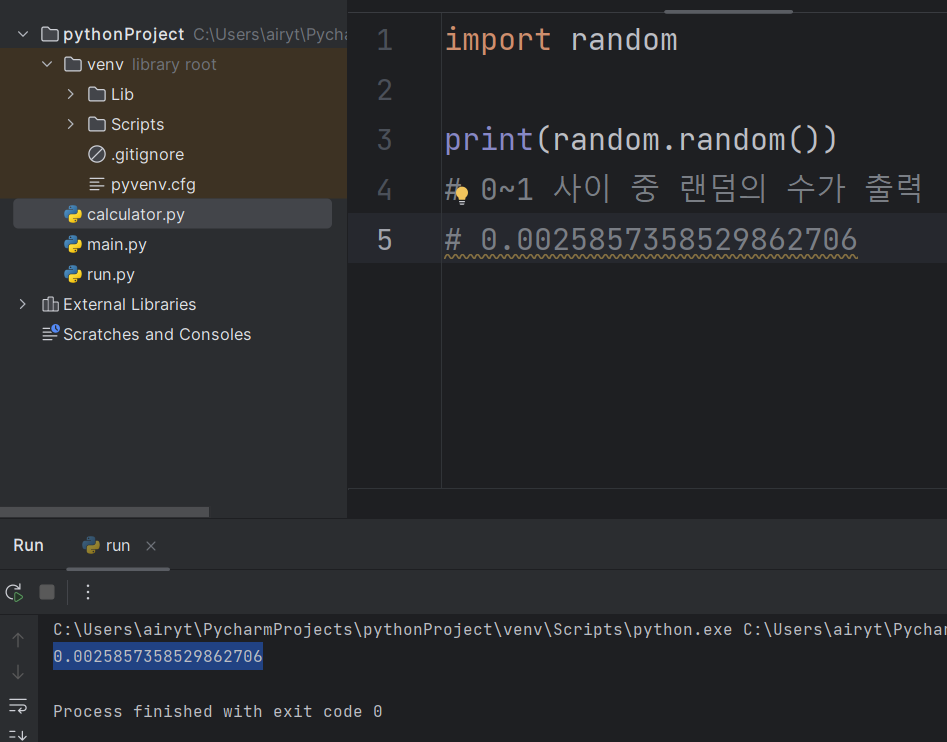
import random
print(random.random())
# 0~1 사이 중 랜덤의 수가 출력
# 0.7612105763848416
random 모듈
import random
"""
randint() 함수
randint(a, b)
a ≤ N ≤ b를 만족하는 어떤 랜덤한 정수 N을 리턴
"""
print(random.randint(1, 20)) # 12
print(random.randint(5, 100)) # 68
"""
uniform() 함수
uniform(a, b)
a ≤ N ≤ b를 만족하는 어떤 랜덤한 소수 N을 리턴
"""
print(random.uniform(0, 1)) # 0.9688231124898523
print(random.uniform(0, 1)) # 0.6065646256435557
datetime 모듈
import datetime
"""
datetime 값 생성
"""
# 2023년 3월 14일
pi_day = datetime.datetime(2023, 3, 14)
print(pi_day) # 2023-03-14 00:00:00
print(type(pi_day)) # <class 'datetime.datetime'>
# 시각은 자동으로 00시 00분 00초로 설정되어 있음.
# 시각을 임의로 변경 가능
pi_day = datetime.datetime(2023, 3, 14, 15, 16, 15)
print(pi_day) # 2023-03-14 15:16:15
print(type(pi_day)) # <class 'datetime.datetime'>
"""
오늘 날짜
코드를 실행한 지금 이 순간의 날짜 불러오기기
"""
today = datetime.datetime.now()
print(today) # 2023-08-01 06:18:54.881155
print(type(today)) # <class 'datetime.datetime'>import datetime
"""
timedelta 타입
"""
"""
두 datetime 값 사이의 기간
숫자 뺄셈으로 연산하기
"""
today = datetime.datetime.now()
pi_day = datetime.datetime(2023, 3, 14, 13, 6, 15)
print(today - pi_day) # 139 days, 17:24:45.524085
print(type(today - pi_day)) # <class 'datetime.timedelta'>
"""
timedelta 생성해서 datetime 값에 더하기기
"""
today = datetime.datetime.now()
my_timedelta = datetime.timedelta(days = 5, hours = 3, minutes = 10, seconds = 50)
print(today) # 2023-08-01 06:33:27.952853
print(today + my_timedelta) # 2023-08-06 09:44:17.952853
"""
datetime에서 여러가지 값 추출
"""
today = datetime.datetime.now()
print(today) # 2023-08-01 06:35:29.810582
print(today.year) # 2023
print(today.month) # 8
print(today.day) # 1
print(today.hour) # 6
print(today.minute) # 35
print(today.second) # 29
print(today.microsecond) # 810582
"""
strftime() 함수
datetime 포매팅
"""
today = datetime.datetime.now()
print(today)
print(today.strftime("%A, %B %dth %Y")) # 2023-08-01 06:37:19.722723 Tuesday, August 01th 2023
# %a, %m 같은 걸 포맷코드라고 함2. 사용자 입력 받기
input
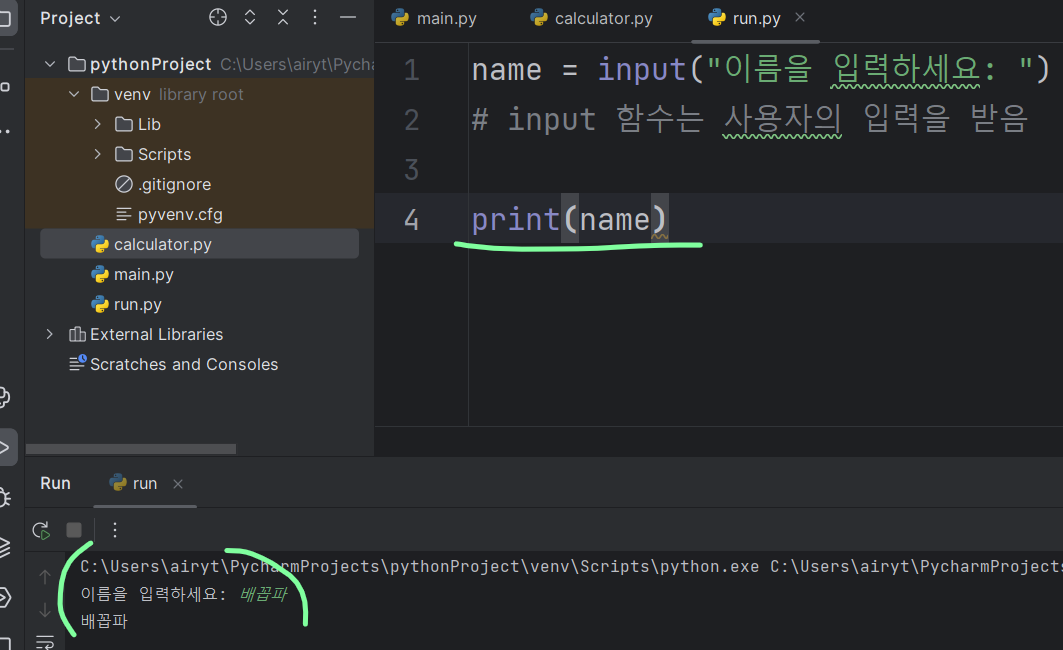
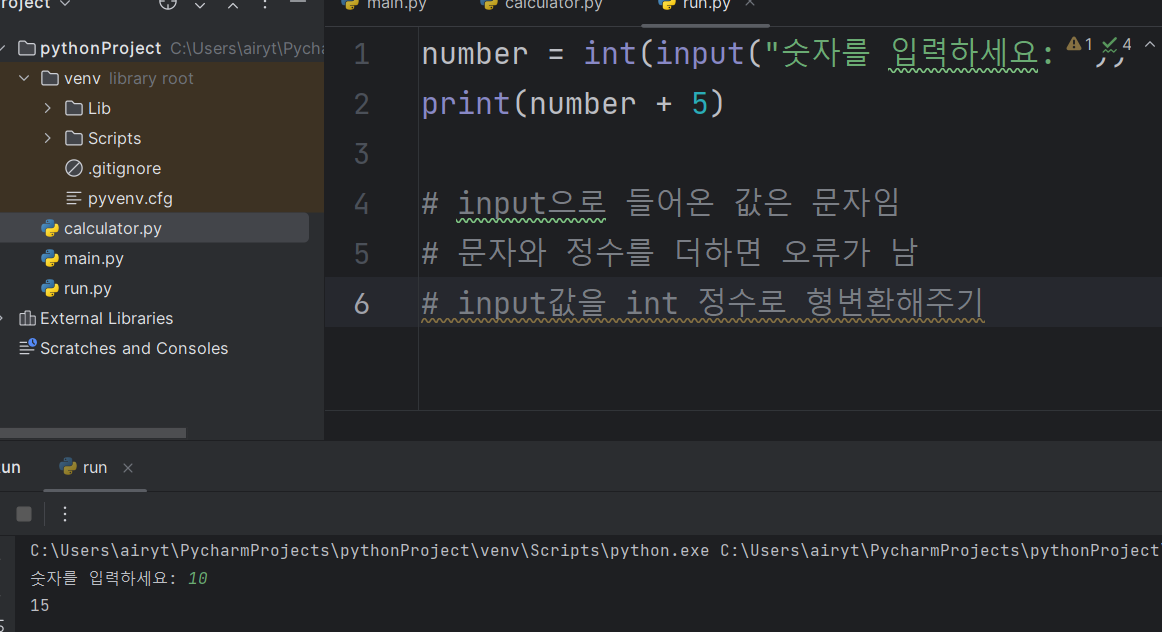
number = int(input("숫자를 입력하세요: "))
print(number + 5)
# input으로 들어온 값은 문자임
# 문자와 정수를 더하면 오류가 남
number = int(input("숫자를 입력하세요: "))
print(number + 5)
# input값을 int 정수로 형변환해주기
숫자 맞히기 게임
1부터 20까지 수 중 랜덤으로 생성하여 총 4번의 기회 동안 사용자가 맞히는 게임
import random
count = 4 # 남은 기회가 총 4번
ans_num = random.randint(1, 20) # 1부터 20까지 정수를 랜덤으로 생성
while count >= 1:
rand_num = int(input("기회가 {}번 남았습니다. 1-20 사이의 숫자를 맞혀 보세요:".format(count)))
# count가 줄어들 때마다 입력을 새로 받아야 함 -> while문 안으로 input함수를 넣어야 함
if ans_num > rand_num:
print("up")
elif ans_num < rand_num:
print("down")
else:
print("축하합니다. {}번 만에 숫자를 맞히셨습니다.".format(4-count))
break
count -= 1
# 어떤 결과가 나오든 남은기회(count)가 하나씩 줄어들도록 해야 함.
if count == 0:
print("아쉽습니다. 정답은 {}입니다.".format(ans_num))import random
# 상수 정의
ANSWER = random.randint(1, 20)
NUM_TRIES = 4
# 변수 정의
guess = -1
tries = 0
while guess != ANSWER and tries < NUM_TRIES:
guess = int(input("기회가 {}번 남았습니다. 1-20 사이의 숫자를 맞혀 보세요: ".format(NUM_TRIES - tries)))
tries += 1
if ANSWER > guess:
print("Up")
elif ANSWER < guess:
print("Down")
if guess == ANSWER:
print("축하합니다. {}번 만에 숫자를 맞히셨습니다.".format(tries))
else:
print("아쉽습니다. 정답은 {}입니다.".format(ANSWER))3. 파일 읽고 쓰기
파일 읽기
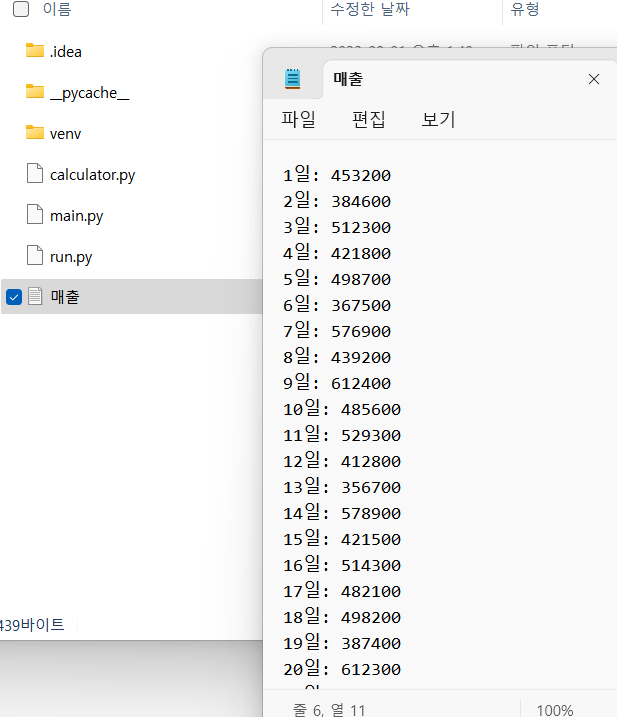
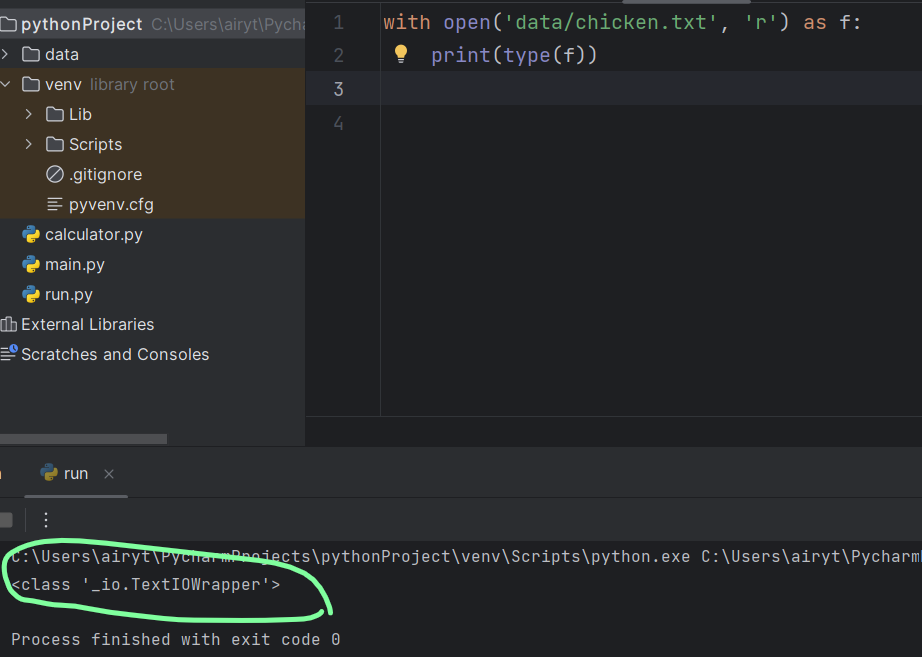
with open('chicken.txt', 'r') as f:
"""
open(파일이름, 문자열 r)
r = read (읽기) / w = write (쓰기)
현재 chicken.txt 파일이 같은 폴더 안에 있어서 경로를 별도로 작성 안 함.
읽어드린 파일은 'f'라는 변수에 저장함.
"""
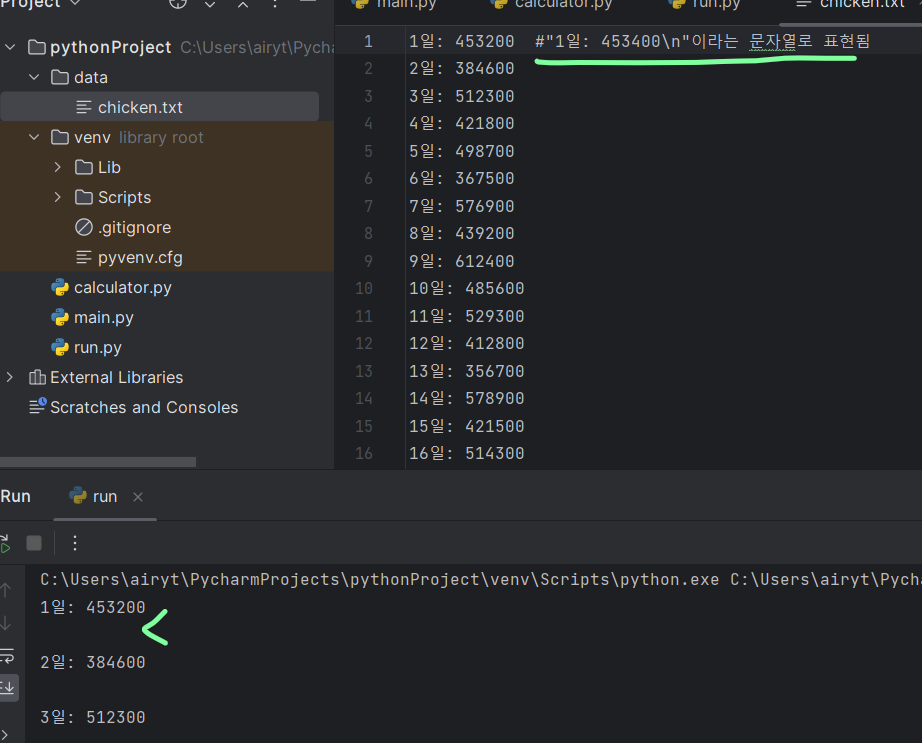
with open('data/chicken.txt', 'r') as f:
"""
현재 chicken.txt 파일이 data 폴더 안에 있음.
"""
with open('data/chicken.txt', 'r') as f:
print(type(f))
# <class '_io.TextIOWrapper'>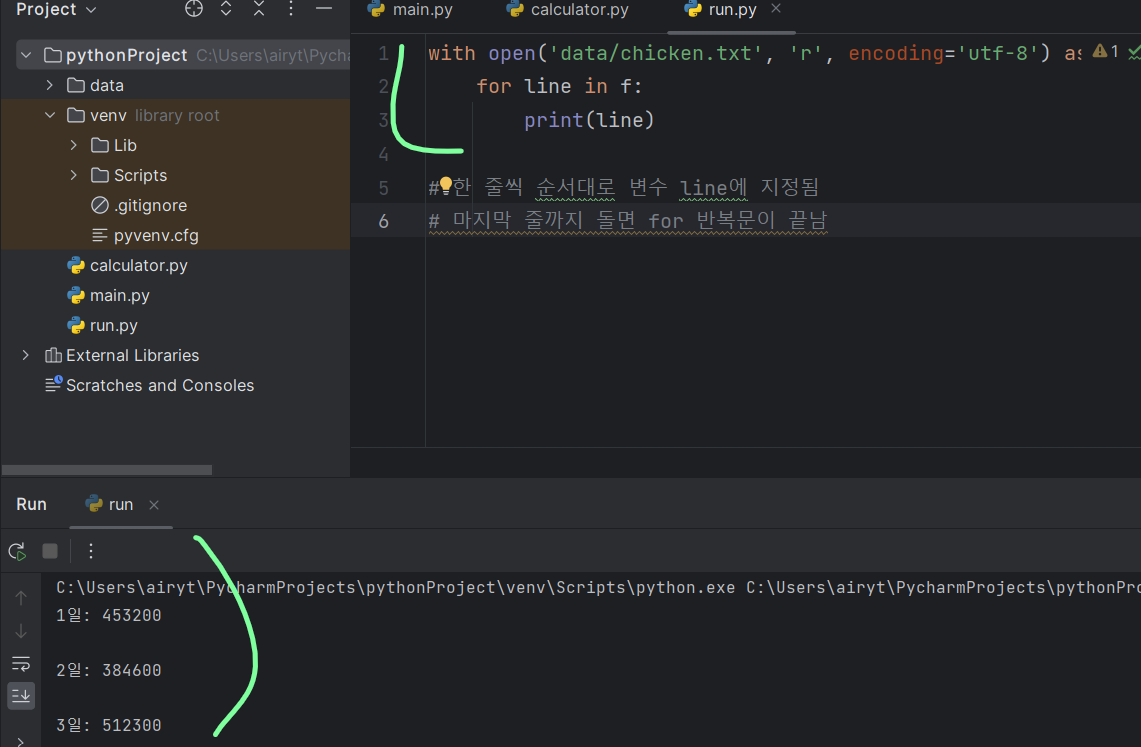
with open('data/chicken.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
print(line)
# 한 줄씩 순서대로 변수 line에 지정됨
# 마지막 줄까지 돌면 for 반복문이 끝남
strip
print("Hello")
print("Hello")
"""
Hello
Hello
"""
print("Hello\n")
print("Hello")
"""
Hello
Hello
"""
# print문은 기본적으로 엔터가 반영(개행된 상태)
# ''\n'을 붙이면 한 줄이 띄어짐"""
strip
문자열의 앞 뒤에 있는 화이트스페이스를 없애줌
화이트스페이스 : "", "\t", "\n"
"""
print(" abc def ".strip())
# abc def (앞 뒤 공백들이 날아감)
print(" \t \n abc def \n\n\n".strip())
# abc def (앞 뒤 화이트스페이스들이 전부 날아감)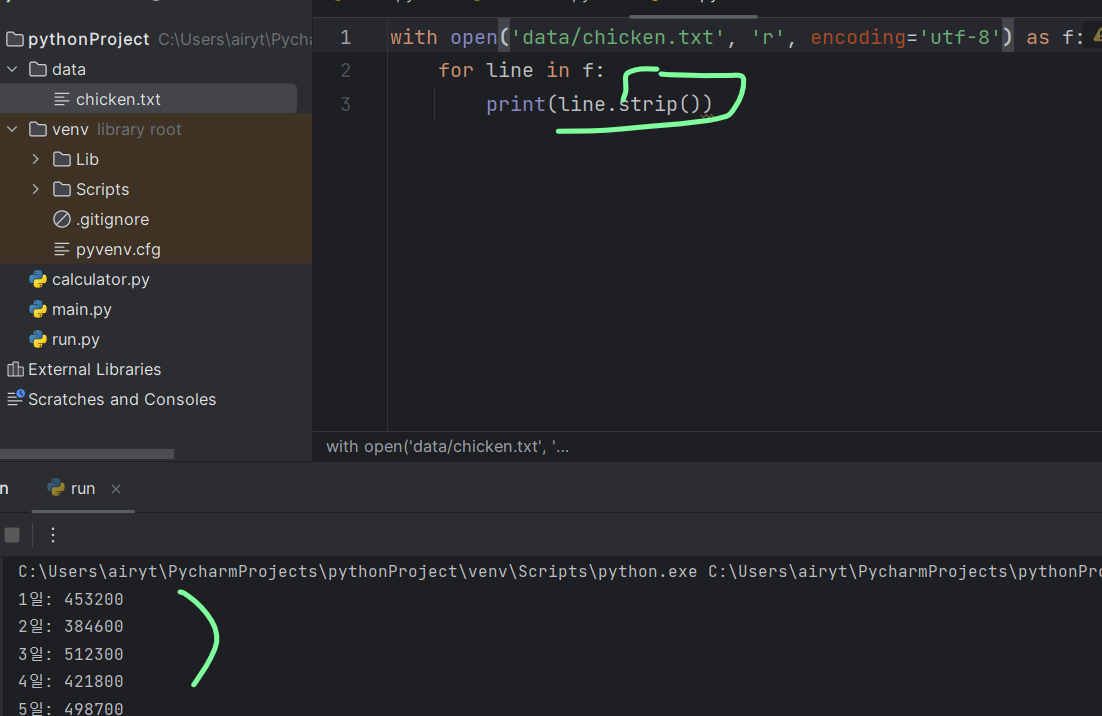
with open('data/chicken.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
print(line.strip()) # 줄마다 있던 공백 제거됨
split
"""
split
해당 파라미터를 기준으로 문자열을 나눔
"""
my_string = "1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6"
print(my_string.split("."))
# ['1', ' 2', ' 3', ' 4', ' 5', ' 6']
"""
거슬리는 띄어쓰기를 없애려면?
문자열 나누는 기준을 ". " (점 띄어쓰기)로 한다
"""
print(my_string.split(". "))
# ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6']
full_name = "Kim, Yuna"
print(full_name.split(","))
# ['Kim', ' Yuna']
# ' Yuna'에 있는 띄어쓰기 없애려면 마찬가지로 ", "를 기준으로 설정
full_name = "Kim, Yuna"
print(full_name.split(", "))
# ['Kim', 'Yuna']
my_name = "hungry_bellybutton"
name_data = my_name.split("_")
last_name = name_data[0]
first_name = name_data[1]
print(first_name, last_name)
# bellybutton hungry
"""
어떤 걸 기준으로 나눠야 할까?
print(" \n\n 2 \t 3 \n 5 7 11 \n \n")
"""
# 화이트스페이스를 기준으로 나누고 싶으면
print(" \n\n 2 \t 3 \n 5 7 11 \n \n".split())
# ['2', '3', '5', '7', '11']
numbers = " \n\n 2 \t 3 \n 5 7 11 \n \n".split()
print(numbers[0] + numbers[1])
# 23
# split을 이용해서 리스트를 만든 값은 모두 "문자열"임!
numbers = " \n\n 2 \t 3 \n 5 7 11 \n \n".split()
print(int(numbers[0]) + int(numbers[1]))
# 5
코딩에 빠진 닭
# 변수
sale_amount = 0 # 매출합
days = 0 # 일자 수
# 파일 열어서 split으로 구분
with open('data/chicken.txt', 'r') as f:
for line in f:
list = line.split("일:")
days += 1
sale_amount += int(list[1])
# 평균 매출액 구하기
ave_sale = sale_amount / days
print(ave_sale)with open('data/chicken.txt', 'r') as f:
total_revenue = 0
total_days = 0
for line in f:
data = line.strip().split(": ")
revenue = int(data[1]) # 그날의 매출
total_revenue += revenue
total_days += 1
print(total_revenue / total_days)line = "19일: 434500\n"
data = line.strip().split(": ")
print(data) # ['19일', '434500']
print(data[1]) # 434500
파일 쓰기
# w(write)모드 = 새로쓰기
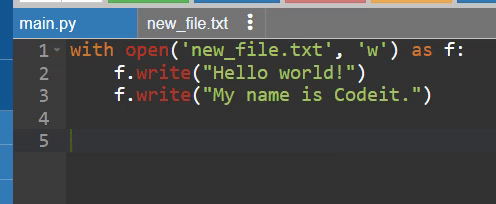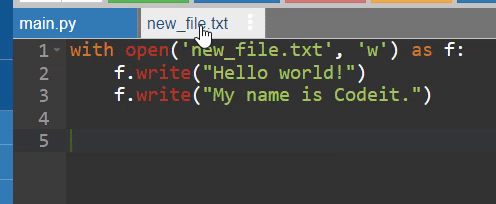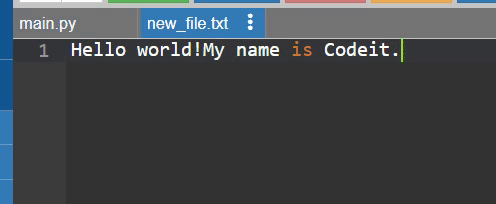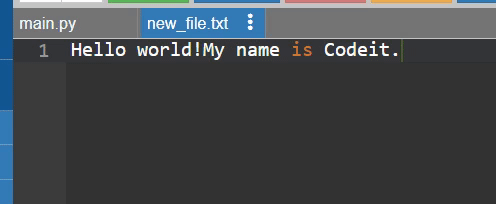
with open('new_file.txt', 'w') as f:
f.write("Hello world!")
f.write("My name is Codeit.")
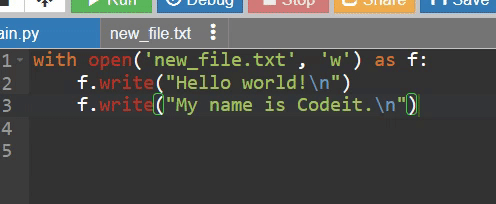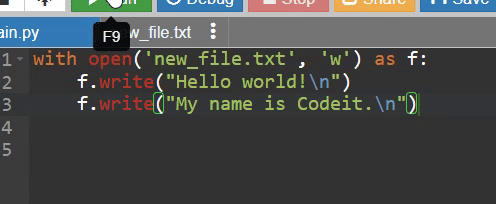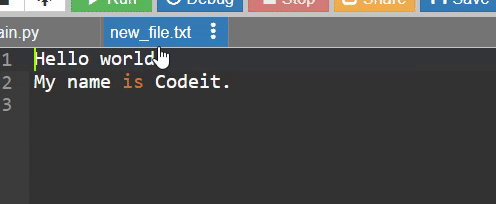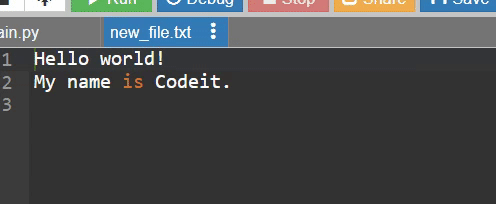
with open('new_file.txt', 'w') as f:
f.write("Hello world!\n") # 개행문자를 넣어서 한 줄씩 띄워줌
f.write("My name is Codeit.\n")
'''
마지막에 작성한 글이 처음에 작성한 글을 덮어씀.
만약 덮어쓰는게 아니라 기존 파일에 추가하고 싶다면?
'''
# a(append)모드 = 추가
with open('new_file.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write("Hello world!\n")
f.write("My name is Codeit.\n")
'''
new_file이 있으면 -> 기존 내용에 추가하기
new_file이 없으면 -> 새로 만들기
'''
단어장 만들기
with open('vocabulary.txt', 'w') as f:
while True:
eng = input("영어 단어를 입력하세요: ")
# q를 입력하면 프로그램 종료료
if eng == 'q':
break
kor = input("한국어 뜻을 입력하세요: ")
# q를 입력하면 프로그램 종료
if kor == 'q':
break
# 파일에 영어:한글 기록
f.write("{}: {}\n".format(eng, kor))
단어 퀴즈
with open('vocabulary.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
data = line.strip().split(": ") # 영/한 단어를 쪼개서 리스트에 한 줄씩 넣어줌
guess = input("{}: ".format(data[1])) # data[1]은 한글
if guess == data[0]: # data[0]은 영어
print("맞았습니다!")
else:
print("아쉽습니다. 정답은 {}입니다.".format(data[0]))
# 한 줄을 split(": ")로 분리했으므로 data 리스트에는 항상 2개의 요소만 들어감.
고급 단어장
import random
voca_dict = {}
with (open('vocabulary.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f):
for line in f:
# key는 사용자가 입력해야 할 영단어
# value는 컴퓨터가 출력해야 할 한글뜻
key, value = line.strip().split(": ")
voca_dict[key] = value
# random.choice()함수를 사용하여 voca_dict.keys() 요소들 중 하나를 랜덤하게 선택
# 딕셔너리 voca_dict의 키(key)들을 리스트로 변환홤.
random_key = random.choice(list(voca_dict.keys()))
# random_key에 맞는 random_value 생성
random_value = voca_dict[random_key]
# 한글뜻 random_value를 주면 사용자가 입력한 단어가 guess에 저장됨
guess = input("{}: ".format(random_value))
if guess != 'q':
if guess == random_key: # 랜덤 생성된 영단어가 guess와 일치하면 맞았다고 출력
print("맞았습니다!")
else: # 틀렸으면 정답을 표시해줌.
print("아쉽습니다. 정답은 {}입니다.".format(random_key))
else: # guess가 q이면 종료
break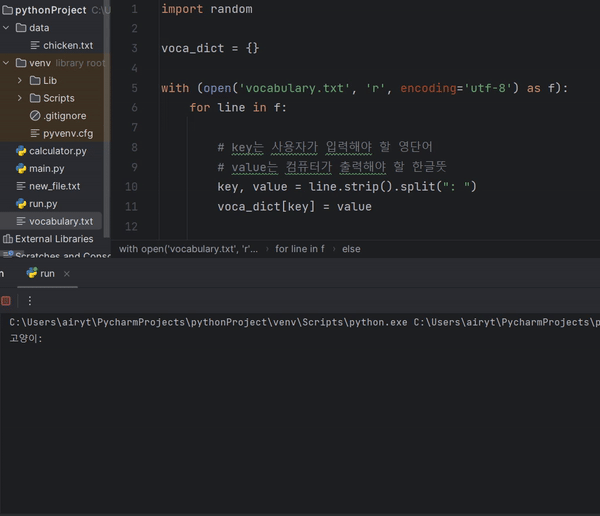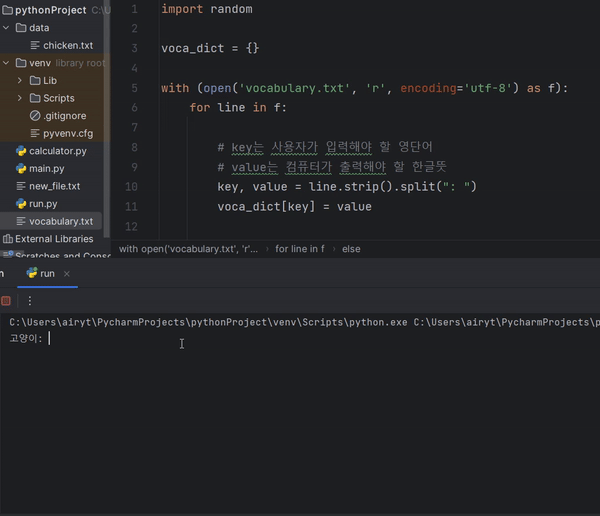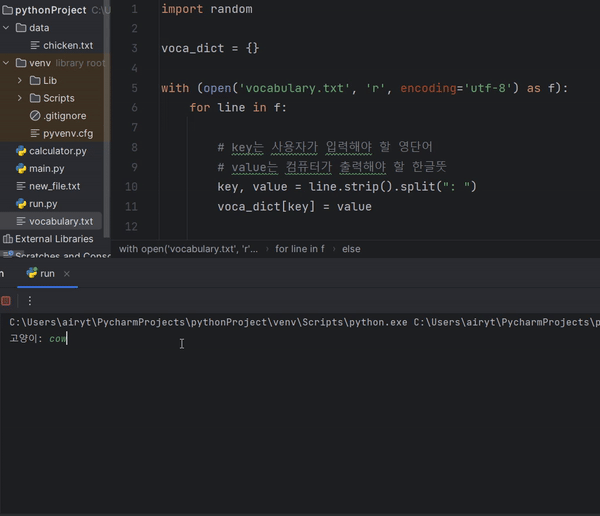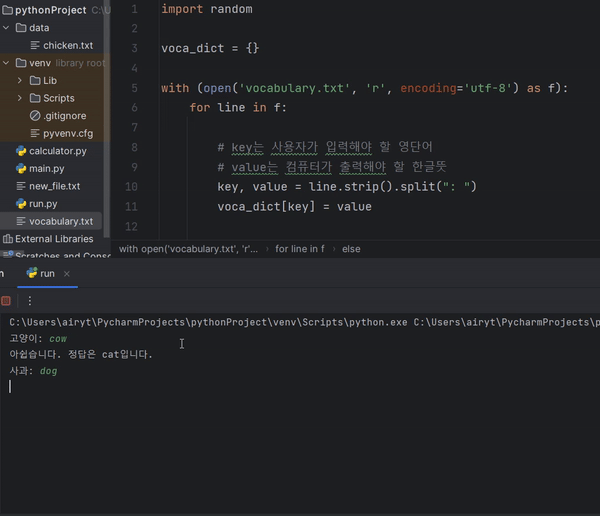
import random
# 사전 만들기
vocab = {}
with open('vocabulary.txt', 'r') as f:
for line in f:
data = line.strip().split(": ")
english_word, korean_word = data[0], data[1]
vocab[english_word] = korean_word
# 목록 가져오기
keys = list(vocab.keys())
# 문제 내기
while True:
# 랜덤한 문제 받아 오기
index = random.randint(0, len(keys) - 1)
english_word = keys[index]
korean_word = vocab[english_word]
# 유저 입력값 받기
guess = input("{}: ".format(korean_word))
# 프로그램 끝내기
if guess == 'q':
break
# 정답 확인하기
if guess == english_word:
print("정답입니다!\n")
else:
print("틀렸습니다. 정답은 {}입니다.\n".format(english_word))4. 프로젝트: 로또 시뮬레이션
로또 시뮬레이션: 1) 번호 뽑기
from random import randint
def generate_numbers(n):
numbers = []
i = 0
while i < n:
number = randint(1, 45)
if number not in numbers:
numbers.insert(i, number)
else:
continue
i += 1
return numbers
# 테스트 코드
print(generate_numbers(6))• 변수 i 대신 리스트의 길이 len()함수를 사용하면 코드가 줄어듦.
왜냐하면 숫자를 하나씩 넣을 때마다 리스트의 길이도 그에 맞게 하나씩 커지니까.
• insert 대신 append를 사용하면 코드가 더 간단해짐.
• 함수 만들었으면 꼭 return값 반환하기
# 모범답안
from random import randint
def generate_numbers(n):
numbers = []
while len(numbers) < n:
num = randint(1, 45)
if num not in numbers:
numbers.append(num)
return numbers
randint 사용 방법
import random
random.randint()
from random import randint
randint()
로또 시뮬레이션: 2) 당첨 번호 뽑기
from random import randint
def generate_numbers(n):
numbers = []
while len(numbers) < n:
num = randint(1, 45)
if num not in numbers:
numbers.append(num)
return numbers
def draw_winning_numbers():
numbers = []
while len(numbers) < 6:
num = randint(1, 45)
if num not in numbers:
numbers.append(num)
new_numbers = sorted(numbers)
while True:
bonus_number = randint(1,45)
if bonus_number not in new_numbers:
new_numbers.append(bonus_number)
break
else:
continue
return new_numbers
# 테스트 코드
print(draw_winning_numbers())• draw_winning_numbers()는 generate_numbers 활용하라고 해서 아무 생각없이 긁어 왔는데 그럴 필요가 없음.
• draw 함수 그대로 (숫자 6개) 정렬시키기 + 숫자 1개 뒤에 이어 붙이기
→ draw 함수에 7을 넣어서 숫자 7개 만들고 슬라이싱 (6개 - 정렬 / 1개)
# 모범답안
from random import randint
def generate_numbers(n):
numbers = []
while len(numbers) < n:
num = randint(1, 45)
if num not in numbers:
numbers.append(num)
return numbers
def draw_winning_numbers():
winning_numbers = generate_numbers(7)
return sorted(winning_numbers[:6]) + winning_numbers[6:])
로또 시뮬레이션: 3) 겹치는 번호 개수
def count_matching_numbers(numbers, winning_numbers):
count = 0
for number in numbers:
if number in winning_numbers:
count += 1
return count
# 테스트 코드
print(count_matching_numbers([2, 7, 11, 14, 25, 40], [2, 11, 13, 14, 30, 35])) #3
print(count_matching_numbers([2, 7, 11, 14, 25, 40], [14])) #1
로또 시뮬레이션: 4) 당첨금 확인
def check(numbers, winning_numbers):
count = count_matching_numbers(numbers, winning_numbers)
if winning_numbers[6] in numbers:
if count == 6:
return 50000000
else:
if count == 6:
return 1000000000
elif count == 5:
return 1000000
elif count == 4:
return 50000
elif count == 3:
return 5000
# 테스트 코드
print(check([2, 4, 11, 14, 25, 40], [4, 12, 14, 28, 40, 41, 6])) # 5000
print(check([2, 4, 11, 14, 25, 40], [2, 4, 10, 11, 14, 40, 25])) # 50000000# 모범답안
def check(numbers, winning_numbers):
count = count_matching_numbers(numbers, winning_numbers[:6])
bonus_count = count_matching_numbers(numbers, winning_numbers[6:])
if count == 6:
return 1000000000
elif count == 5 and bonus_count == 1:
return 50000000
elif count == 5:
return 1000000
elif count == 4:
return 50000
elif count == 3:
return 5000
else:
return 0
# 테스트 코드
print(check([2, 4, 11, 14, 25, 40], [4, 12, 14, 28, 40, 41, 6]))
print(check([2, 4, 11, 14, 25, 40], [2, 4, 10, 11, 14, 40, 25]))• 함수 슬라이싱을 이용하여 count와 bonus_count 변수를 만들었음.
로또 시뮬레이션: 5) 코드 하나로 합치기
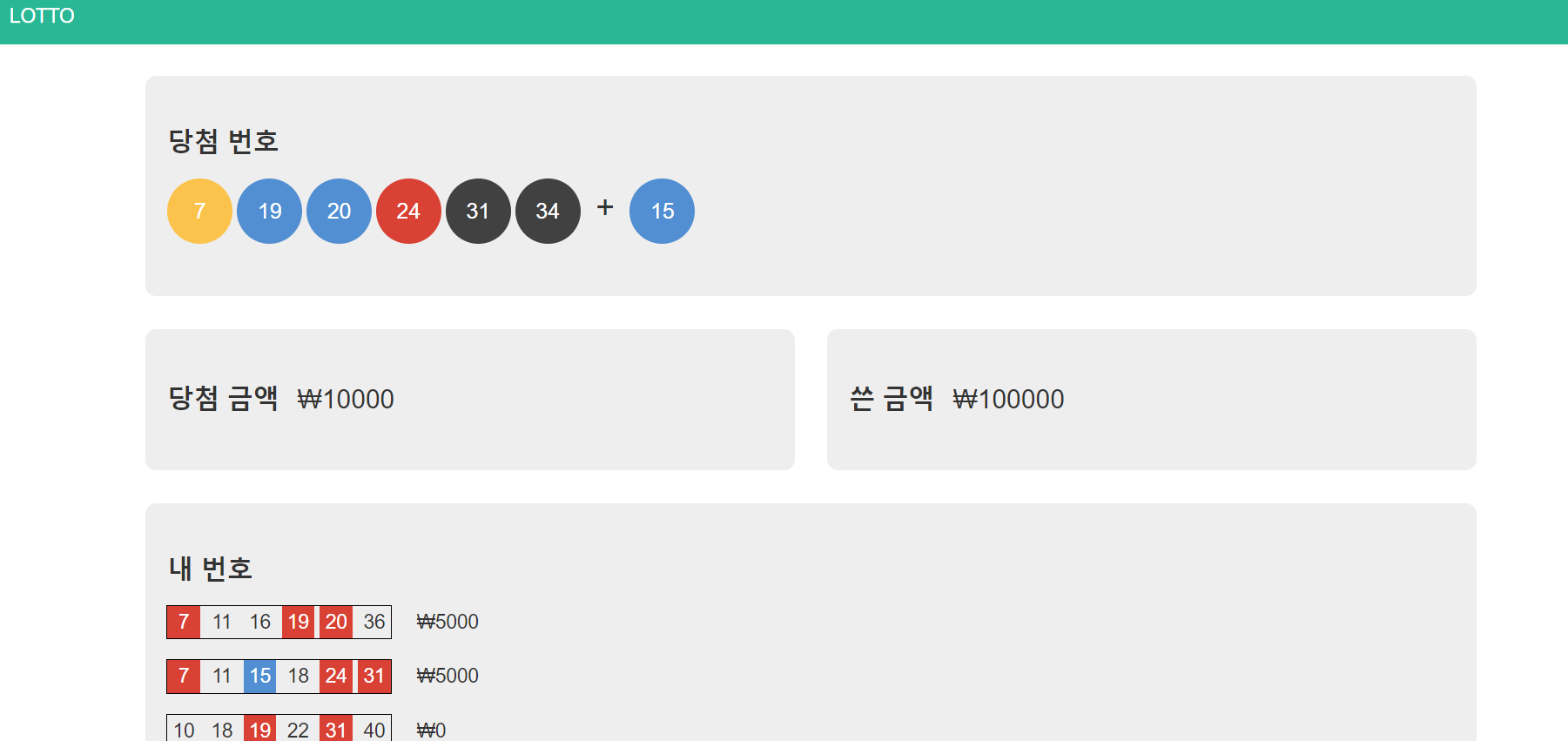
5. 프로젝트: 숫자 야구
숫자 야구: 코드 하나로 합치기
from random import randint
# 랜덤으로 숫자 생성
def generate_numbers():
numbers = []
i = 0
while i < 3:
a = randint(0, 9)
if a not in numbers:
numbers.insert(i, a)
i += 1
print("0과 9 사이의 서로 다른 숫자 3개를 랜덤한 순서로 뽑았습니다.\n")
return numbers
# 숫자 예측
def take_guess():
print("숫자 3개를 하나씩 차례대로 입력하세요.")
new_guess = []
i = 0
while i < 3:
num = int(input("{}번째 숫자를 입력하세요: ".format(i)))
if num < 0 or num > 9:
print("범위를 벗어나는 숫자입니다. 다시 입력하세요.")
else:
if num not in new_guess:
new_guess.append(num)
i += 1
else:
print("중복되는 숫자입니다. 다시 입력하세요.")
return new_guess
# 점수계산
def get_score(guesses, solution):
strike_count = 0
ball_count = 0
i = 0
while i < len(guesses):
if guesses[i] in solution:
if guesses[i] == solution[i]:
strike_count += 1
else:
ball_count += 1
i += 1
return strike_count, ball_count
# 여기서부터 게임 시작!
ANSWER = generate_numbers()
tries = 0
while True:
guess = take_guess()
strike, ball = get_score(guess, ANSWER)
tries += 1
print("{}S, {}B".format(strike, ball))
if strike == 3 and ball == 0:
print("축하합니다. {}번 만에 숫자 3개의 값과 위치를 모두 맞히셨습니다.".format(tries))
break
# 모범답안
from random import randint
def generate_numbers():
numbers = []
while len(numbers) < 3:
new_number = randint(0, 9)
if new_number not in numbers:
numbers.append(new_number)
return numbers
def take_guess():
new_guess = []
while len(new_guess) < 3:
num = int(input("{}번째 수를 입력하세요: ".format(len(new_guess) + 1)))
if num < 0 or num > 9:
print("0에서 9까지의 수를 입력해 주세요!")
elif num in new_guess:
print("중복되는 숫자입니다. 다시 입력하세요.")
else:
new_guess.append(num)
return new_guess
def get_score(guesses, solution):
strike_count = 0
ball_count = 0
for i in range(3):
if guesses[i] == solution[i]:
strike_count += 1
elif guesses[i] in solution:
ball_count += 1
return strike_count, ball_count
# 여기서부터 게임 시작!
ANSWER = generate_numbers()
tries = 0
while True:
user_guess = take_guess()
s, b = get_score(user_guess, ANSWER)
print("{}S {}B\n".format(s, b))
tries += 1
if s == 3:
break
print("축하합니다. {}번 만에 세 숫자의 값과 위치를 모두 맞히셨습니다.".format(tries))
728x90